Some financial markets have seasonal patterns that can form the basis for automated strategies. The idea behind bias systems is to intercept and exploit recurring movements of a financial instrument within precise time horizons. In this article, we’ll look at how to unearth such trends and in which markets these strategies work best. In addition, we’ll show you two examples of well-performing bias systems on Gold Futures.
What Are Biases
In trading, the term “bias” denotes repetitive behaviors of a market that can be exploited with trading systems.
Some Futures, for example, often show a tendency to move up or down in certain time slots, days of the week, or months of the year.
The idea behind the bias systems is to build programs that can exploit seasonal market patterns.
It’s as if you have a colleague who leaves his newspaper on his desk every day from 12 noon to 1 p.m. to go to lunch. Knowing this habit, you could take advantage and read his newspaper for free at this time each day!
There are different types of bias, classified according to the time horizon being considered. We can analyze trends and recurring behaviors within months of the year, days of the month, the week, or, even, within hours of the day.
How a Bias Strategy Works
As mentioned above, bias systems exploit trends that occur with a regular cadence on a certain financial instrument or portfolio of multiple underlying assets. If, for example, we notice that every day between 10 a.m. and 11 a.m. an instrument price tends to decrease, we might assume that the same behavior will also occur the following day.
It’s precisely the “repetitiveness” of a movement on the chart that, once it becomes statistically robust, makes it possible to build reliable trading systems.
In practice, those who follow this approach analyze the behaviors of a financial instrument over different time frames and try to understand whether the underlying asset has average trends that recur regularly inside the time frames being analyzed.
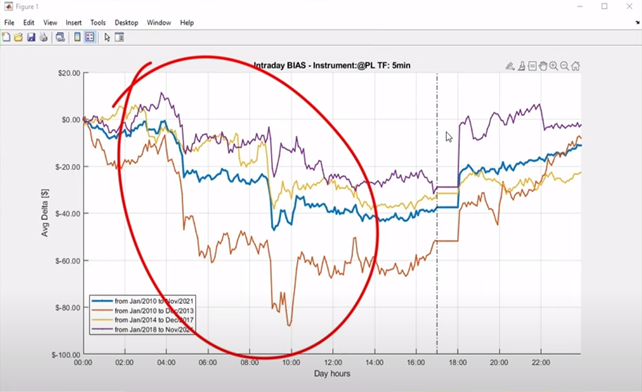
Intraday bias on Platinum.
Based on the time reference taken into consideration, we can have:
- Intraday bias: It’s the most widely used bias system. As the name suggests, intraday bias systems exploit repeating price trends at certain times of the day. To check for intraday bias, simply create a script that buys at the beginning of each hourly bar of the day and closes the trade at the close of that bar.
- Intraweek Bias: It consists of checking whether a financial instrument goes up or down for some consecutive days or portions of the stock market week. To do this, simply calculate the average price changes for each day of the week.
- Intramonth Bias: It consists of looking for exploitable trends within the business month. As with intraweek biases, the analysis is done by calculating average price changes for each day within the month. The average trend can be calculated on all days of the month (and in this case, there will be days, such as holidays, where there is no data) or only on working days.
- Seasonal Bias: It looks for regular seasonal market patterns within the year. This type of bias is the least frequent because it identifies only a few signals within an entire year. If the last few decades are analyzed, the exploitable occurrences are very small.
An analysis can be done using the most common trading platforms such as MultiCharts or TradeStation, which allow data to be exported and then processed with Excel, or through some specific applications such as MatLab, Octave, or Python.
It should be pointed out that, with all trading strategies, including bias systems, it’s only possible to make tests and assumptions based on the statistical behavior of the markets. You can never be certain how a financial instrument will move.
In Which Markets Should Bias Systems Be Used
Bias strategies can be applied effectively to very liquid markets such as Soybeans, Crude Oil, or Heating Oil. Ethereum also has a very interesting intraday bias that few people know about which can be exploited to create very promising automated strategies.
Another example is the gold market. Gold Futures are an extremely liquid market that is well suited to several types of strategies, including trend-following, reversal, and bias. In particular, during certain time frames, the gold market has repetitive movements that are extremely appealing for those wishing to build bias strategies.
In the video below, one of our coaches at Unger Academy shows you two bias strategies on Gold that performed very well in 2022 thus far. The first is a strategy developed over 60 minutes that enters at breakouts at predetermined time slots. The second, on the other hand, works on 5-minute bars.
By watching the video, you’ll discover the equity lines and real performance of these strategies, which, although they relate to specific periods, may still be useful to you in the future for ideas and operational insights.
… So don’t miss it!
Conclusion
Bias systems aim to intercept and exploit the repetitive behavior of a financial instrument or portfolio of underlying assets within a given time horizon. Depending on the period under consideration, it’s possible to have intraday bias, intraweek bias, intra-month bias, or seasonal bias systems.
These strategies are well suited to very liquid markets such as Gold Futures or Ethereum, which have very appealing intraday biases.
The statistical repetitiveness of the movement of a financial instrument allows for predictive analyses of its future behavior.
Of course, these are analyses that, no matter how supported by solid statistical data, are always within the realm of hypotheses. Remember that no strategy can ever predict with certainty how the market will move in the future, so always be wary of those who make such claims!